
The key tenets of 5G
5G has garnered a lot of hype recently as many wireless carriers began their first deployments. In the United States, all major carriers including Verizon, AT&T, Tmobile/Sprint have early deployments in select markets. Carriers worldwide are adopting it as the next generation wireless global standard. Here at NKN, we are excited about the promises of 5G as it brings new underlying technologies that are complementary to NKN.
This new network architecture incorporates:
- Increased speed and low latency - Directly contributes to throughput and latency improvements for NKN nodes running on 5G networks
- Edge Computing - Application hosting resources at the network edge where NKN can offer more points of presence while maximizing edge computing utility
- Network Slicing - Carriers can now share network resources with NKN without exposing the entire network
High speed and low latency
First of all, The most talked about feature of 5G is its improvements in speed and latency. Who doesn’t like faster downloads and quicker network response times, right? Since NKN is an overlay network, we rely on the underlying architecture for data transmission. NKN nodes that use 5G instead of 4G LTE connectivity will have a greater chance to earn rewards from additional NKN services such as nCDN (Content Caching and Video Streaming) and TUNA (Game Streaming and more) where network performance is critical for customer experience. Also, having nodes with better mobile network connectivity strengthens many of NKN’s use cases including shared hotspot coverage via mobile phones and IoT Smart Cities.
| 4G LTE | 5G | |
|---|---|---|
| Max Speed | 150Mbps | 1 - 10Gbps |
| Average Speed | 10Mbps | 50Mbps and up |
| Latency | 50ms | 1ms |
Edge Computing
With the adoption of Edge Computing, 5G network architecture is now more decentralized than ever before. That’s a good thing. NKN has long touted the benefits of having a truly decentralized network for reliability, scale, and privacy.
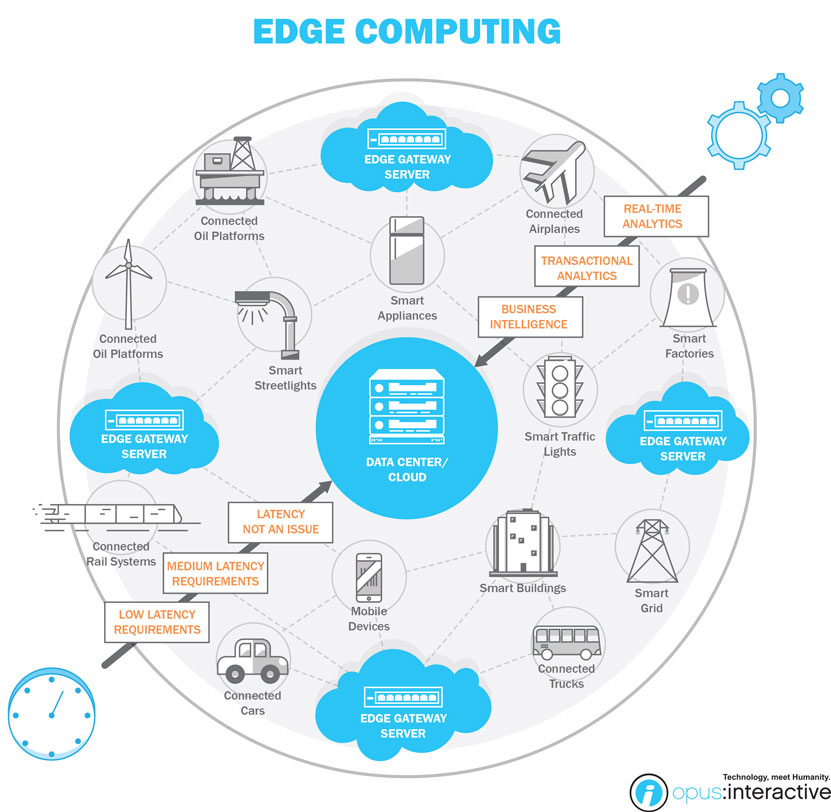
Edge Computing is also critical to support the high throughput and lower latency expectations for 5G that will enable new gaming, IoT, and autonomous driving applications. It allows applications to be run at edge locations closer in proximity to the user. However, these expensive and vital edge resources need to be maximized for the carrier and for the customer. NKN offers a new business model for Edge Computing and provides carriers a way to manage and monetize unused edge resources by sharing these resources with the NKN ecosystem. For more than a year, NKN has been a member of Facebook Telecom Infrastructure Project (TIP) and participates in both the Edge Computing and Edge Application Developer work groups to drive innovation in this market. Edge computing together with NKN are a great way to offer 5G service with maximum utility.
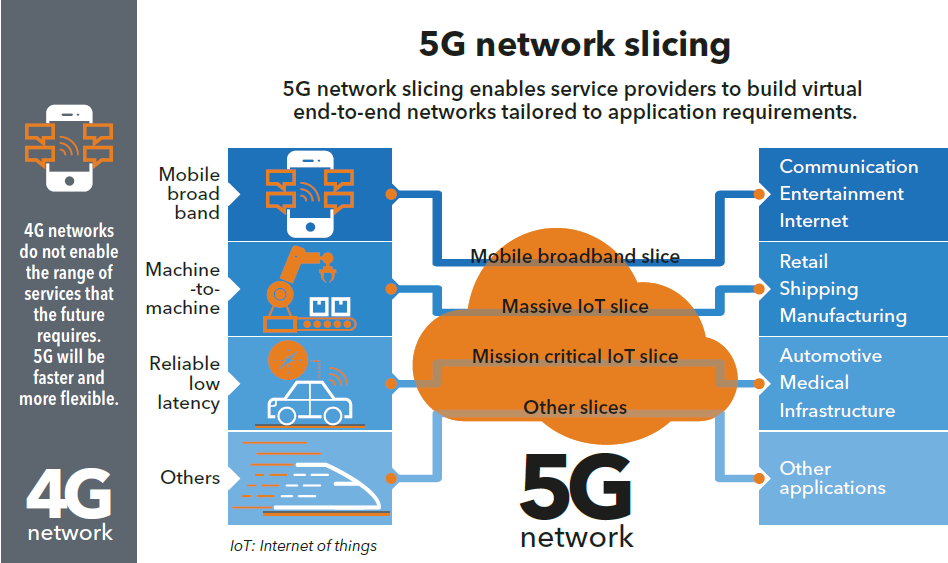
Network slicing and sharing
5G also introduces a new network slicing architecture that allows the underlying infrastructure to be shared to create logically independent virtual networks. These new Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNO) can be customized to meet the demands of many different applications and services. MVNOs are similar in structure to NKN’s crowd-sourced overlay network. NKN creates an independent virtual network on top of existing infrastructure by using unused bandwidth shared by thousands of users. In fact, network slicing can help NKN extend our networking into mobile carrier infrastructure without the risk of exposing their entire network to the public. With network slicing, 5G carriers can now create a MVNO featuring a NKN Full Node that can be shared with NKN’s public network. In this way, carriers can share unused bandwidth for rewards and NKN can offer mobile access for its users.
Source: ITUNews
What 5G can NOT do: a mythbuster
With all of the excitement around 5G, many claim the technology can do almost anything and replace many other technologies. This is simply not true. Here are just a few things 5G can NOT do:
5G will not replace Home Broadband and WiFi
One of the first use cases for 5G deployments by carriers such as Verizon is Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) to provide home broadband. Instead of a cable being connected to your home, a wireless receiver is placed at or near a window in your home to receive a 5G signal and relay it to a home wifi router for your internet connection. The problem here is that 5G frequencies, especially the new millimeter wave band (24–86 GHz) are not very good at indoor coverage and require many more densely populated cell sites installed to provide a good signal to most homes. Even in locations where its available, 300Mbps is the published throughput which does not offer faster service than traditional home broadband today.
Another issue is devices. Other than mobile phones, we don’t expect to see 5G modems as standard options for laptops and home IoT devices due to the additional chip and licensing costs. Therefore, WiFi will still be the choice for indoor coverage for years to come.
5G will not be available everywhere
It will take many years for 5G to be available nationwide and some rural areas may never see 5G. Due to the cell site density needed, it will be costly to support 5G in rural areas. Therefore, we will have a mix of 4G/5G connectivity for the foreseeable future.
5G will not be 100x faster than current 4G
While theoretically 5G could reach out to 10Gbps, the real world customer experience will be a much lower 50Mbps and up. In contrast, AT&T, Verizon, and Tmobile offer 4G LTE downloads around 29Mbps. This means 5G will be noticeably faster, but not revolutionary.
Conclusions
Given these 3 reasons, 5G will continue to be available alongside home broadband (cable, fiber), WiFi, 4G LTE and other connectivity options for years to come. Unfortunately, these networks are often operated by different companies and switching between networks requires separate subscription accounts, authentication, and billing.
NKN can help alleviate this problem. NKN is an overlay network that enables network capacity sharing, and can run on any infrastructure including all types of wireless (WiFi, 3G, 4G, 5G) and wireline (optical, copper) to provide our users a ubiquitous internet connection experience. By using NKN, applications can have access to the best connection available as well as aggregate all types of Internet connection for higher speed and lower latency. NKN can do it already today without waiting for 5G to be deployed everywhere.
Naturally adding 5G to the mix will make NKN work even better, especially in terms of enabling those new applications (e.g. autonomous driving, video streaming) that require super high bandwidth and super low latency. Therefore we are really motivated to work with industry leaders in 5G, including mobile carriers, 5G equipment vendors, and application developers to make 5G and the New Kind of Network shine together. Please contact us ([email protected]) for technical and business collaboration opportunities.
About NKN
NKN is the new kind of P2P network connectivity protocol & ecosystem powered by a novel public blockchain. We use economic incentives to motivate Internet users to share network connection and utilize unused bandwidth. NKN’s open, efficient, and robust networking infrastructure enables application developers to build the decentralized Internet so everyone can enjoy secure, low cost, and universally accessible connectivity.

Home: https://nkn.org/
Email: [email protected]
Telegram: https://t.me/nknorg
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NKN_ORG
Forum: https://forum.nkn.org
Medium: https://medium.com/nknetwork
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/nknetwork/
Github: https://github.com/nknorg
Discord: https://discord.gg/yVCWmkC
YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/c/NKNORG
References:
https://www.sdxcentral.com/5g/definitions/5g-network-slicing/
