nMobile secure messaging app - a Web 3.0 example by NKN.org
Introduction
There is much news and buzz about Web 3.0, but the concept seems to be quite vague or complicated. One impression of Web 3.0 is that it will replace the current Internet, but exactly how is not clear for many people .
There are other more sensational news about Decentralized Finance (DeFi) in 2021 and Non Fungible Tokens (NFT) in 2022, either claiming a sky-high yield or promoted by celebrities. Those types of news might give web 3.0 a bit of a hype reputation.
But today, we are going to talk about a very tangible Web 3.0 example: a chat and messaging app. Almost everyone uses these services every day, ranging from the most popular cellular text message (SMS), WhatsApp, WeChat, iMessage, and Facebook Messenger to more recent exotics such as Telegram and Signal. The popularity is staggering, as you can see from the monthly active users of top messaging apps:
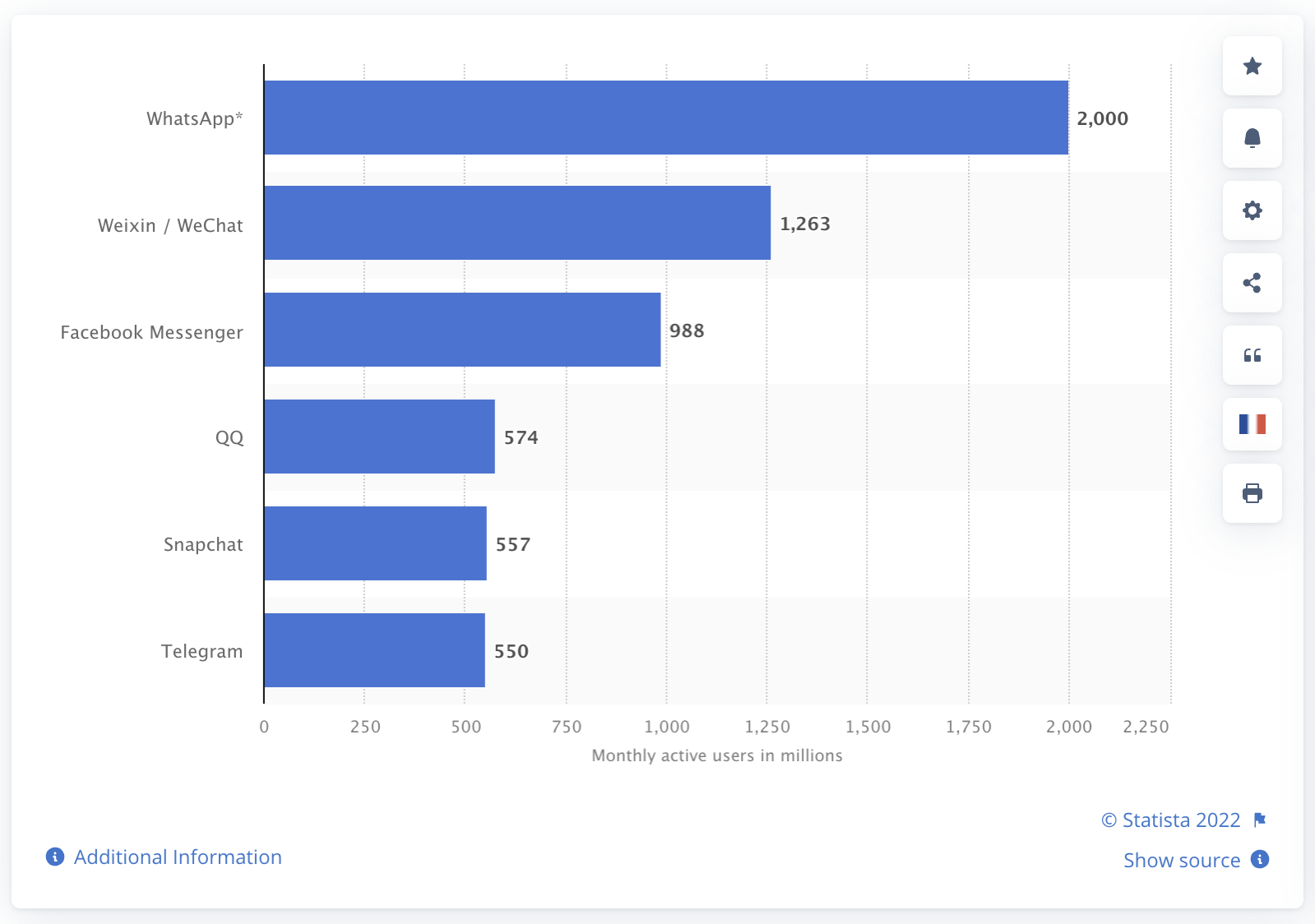
Messaging app global user number (Statista)
So are there any needs for a new kind of messaging app? What can Web 3.0 bring to the table, when it is already kind of full?
Issues with popular chat apps
You might protest, “My current chat app is working just fine, and I heard they just added end-to-end encryption. Wouldn’t that be enough? Why do you need to invent yet another chat application?”
Well, the reality might not be as rosy. Here are just a few recent security and privacy incidents reported in major news. The actual scope of security and privacy breaches might far exceed what we know.
- WhatsApp Fined $266 Million Over Data Transparency Breaches
- WhatsApp Data Breach 2021 Could Expose 2 Billion Users
- Fleeing WhatsApp for Better Privacy? Don’t Turn to Telegram
- Messaging Apps Have an Eavesdropping Problem: Vulnerabilities in Signal, Facebook Messenger, Google Duo, and more all point to a pervasive privacy issue.
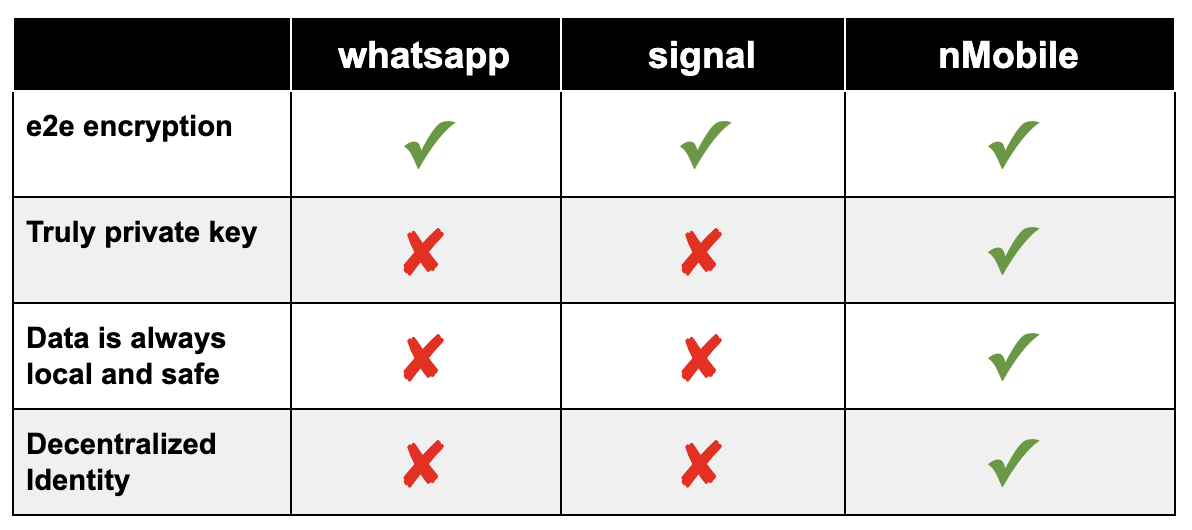
Security & privacy comparison of popular chat app
There are many reasons why popular messaging chat apps are not as secure or private as you thought. But the most important one is that the need to monetize user data is built into the fundamental business model for large Internet companies like Facebook, which owns WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger.
Related: Is WhatsApp Safe? Here’s What You Need to Know | NKN
Key design goals of Web 3.0 chat
Some of the design goals for nMobile, a Web 3.0 chat, are to become the most secure and private chat for communication. To achieve that goal, we need to break down the requirements into a few categories:
- Secure identity: can you remove all personal, identifiable information from the chat communication? For example, not only removing your real name and home address from your chat identity but can you also remove the link to your phone number and other social network presence? Or, going one step further, can you remove your IP address which can indirectly identify your physical location.
- Secure communication: the messages, files, and voice/video communication should be encrypted, and no 3rd party should be able to intercept, eavesdrop, or modify the communication content.
- Secure storage: all the historical messages and files should be encrypted and only stored on the user’s devices and not on any 3rd party servers that could be compromised.
- Fully open source: all nMobile apps’ source code should be open source. Less understood by consumers because the benefits are less tangible. Full open source means that any technically savvy 3rd party can inspect and audit the app, to ensure it does not contain any malware, hidden back doors, or advertisement. In addition, even if the original development team abandons the app, it is still possible for another developer to pick up and maintain the app.
The fundamental shift from all the existing messaging services is that instead of “Don’t be evil,” now it is “Can’t be evil.” Thus we are removing the 3rd party that we have to previously trust, but time and time again not only failed but also exploited the users.
For reference, you can also check a blog post “Messaging app security: Which are the best apps for privacy?” by Kaspersky.
The tech under the hood
nMobile, the Web 3.0 secure chat, is powered by the NKN blockchain and the global peer-to-peer network, But why do we even need a blockchain for sending messages? There are a few crucial building blocks: account and peer-to-peer network.
Account
Just like your phone number can be your WhatsApp account identifier, nMobile uses nMobile ID (NKN address) as your user identifier. Each nMobile account has two parts:
- Your nMobile ID, which is the same as NKN public key. This is visible to your friends and chat buddies. Your nMobile ID is different from your phone number or any other personal identifiable information.
- Your private key: this is your secret and should never be shared with anyone. Its use is to authenticate your identity and encrypt your communication.
Peer-to-peer network
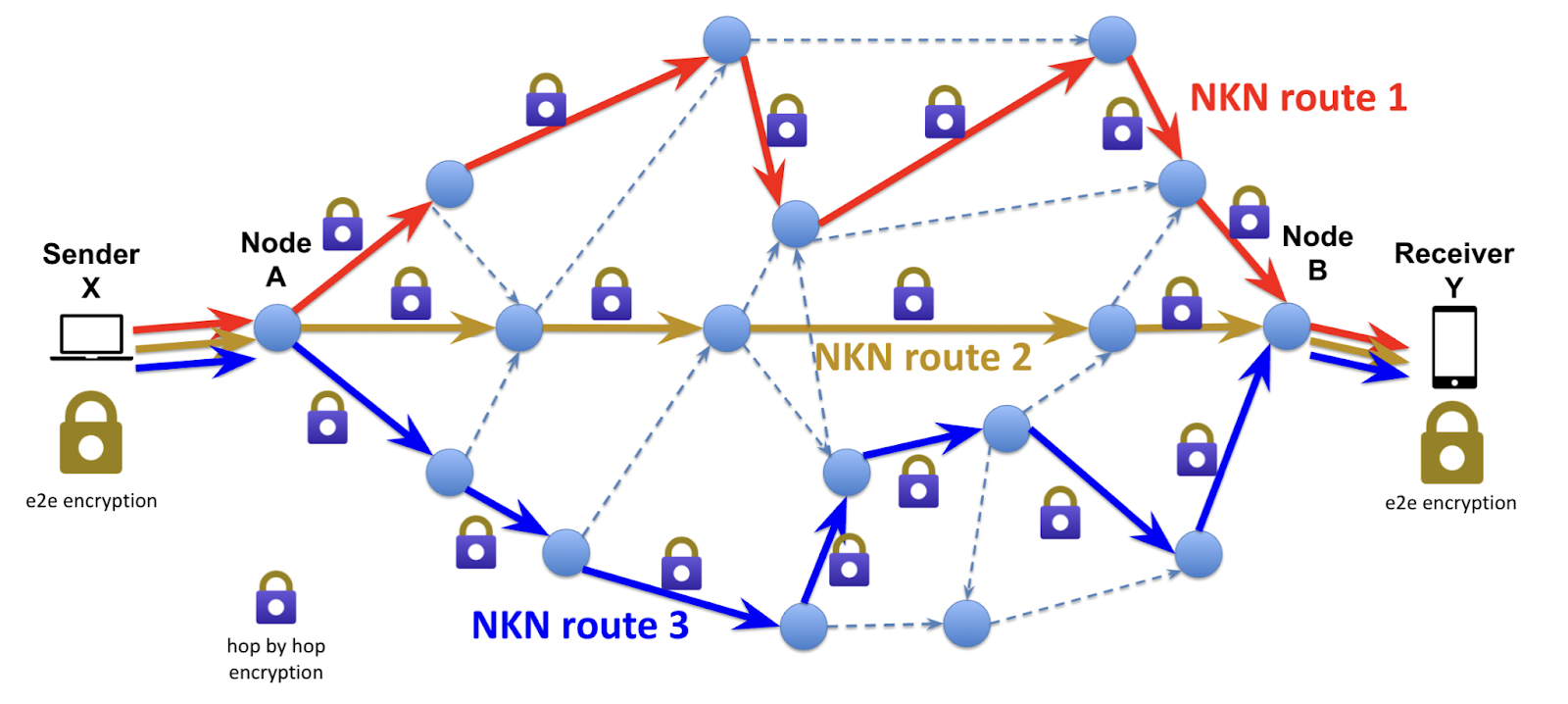
NKN peer to peer network
NKN has one of the largest peer-to-peer networks in the world, with more than 150,000 servers globally in over 50 countries and regions. All of these servers are purely relaying data on behalf of the network, without knowing what the data is. The reason is that any communication between any two NKN users are
- Encrypted end-to-end: your nMobile encrypt every message using your private key
- Encrypted hop-by-hop: even Internet service providers cannot listen in on the communication between NKN relay servers.
- Randomized route: typically, each nMobile message will go through a few randomized hops before reaching your chat buddy.
- Multiple independent paths: additionally, each nMobile app will keep a few alternative routes open all the time. Thus messages can go through different paths and different groups of relay servers.
- In addition, your nMobile ID is not associated with your IP address which could reveal your physical address and location.
If you are interested in understanding more about NKN’s fundamental technology, you might find “NKN In A Nutshell: A Blockchain Powered Communication Network” useful.
Secure local storage
Since all user data are now stored only on their smartphones, it is critical to secure local storage as well. There are two parts:
- Secure storage of accounts, secret key and password. There are Keychain for iOS and Keystore for Android. They should be used whenever possible.
- Secure storage of message database with strong encryption
Are there any drawbacks?
There is no free lunch. In order to maximize the security and privacy of the chat application, we have to give up some convenience.
One of the conveniences that users of nMobile will give up is linking the messaging app with their phone number or using their phone book to discover and connect with other users of nMobile. In order to send the first message to their contact, nMobile needs to use another communication method to share the nMobile ID. For example, scan each other’s QR code when meeting in person. Or send a coded message with a courier pigeon, if you happen to have one.
In addition, the users will have to take the entire responsibility for backing up, managing their own security, and securing their accounts. Since each user’s communication records are entirely kept in their own devices, they need to take the initiative to back up their device regularly. In addition, nMobile users need to actively back up their accounts since there is no centralized entity to recover them (like “Forgot password” for your bank account or WhatsApp messenger).
Securing our privacy for the future

Family looking into better future
With uncertainty and turbulence in today’s world and frequent security breaches within large corporations, we value more and more the privacy and security of our personal communications. Therefore, you might want to think more about which messaging app to trust. And nMobile, as a Web 3.0 example, might well be worth a try if you truly value your privacy and security above convenience.
You can dicover nMobile for iOS and Android here:
